In the modern medical system, medical disposable syringes, as typical representatives of disposable medical products and disposable medical consumables, play a vital and pivotal role in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical operations. From routine vaccination to complex clinical treatments, they are omnipresent, providing fundamental support for the smooth progress of medical work.
Overview of Medical Disposable Syringes
Medical disposable syringes are specifically designed for medical use and are discarded after use to avoid the risk of cross – infection. Their main structure includes a transparent barrel, a push – able piston, a slender plunger, and a sharp needle. The barrel is clearly marked with scales, which is convenient for medical staff to accurately draw and inject liquid medicine. High – quality plastics are mostly selected as materials to ensure non – toxicity, harmlessness, and good toughness and transparency. The needle is made of stainless steel to ensure its sharpness and puncture performance.
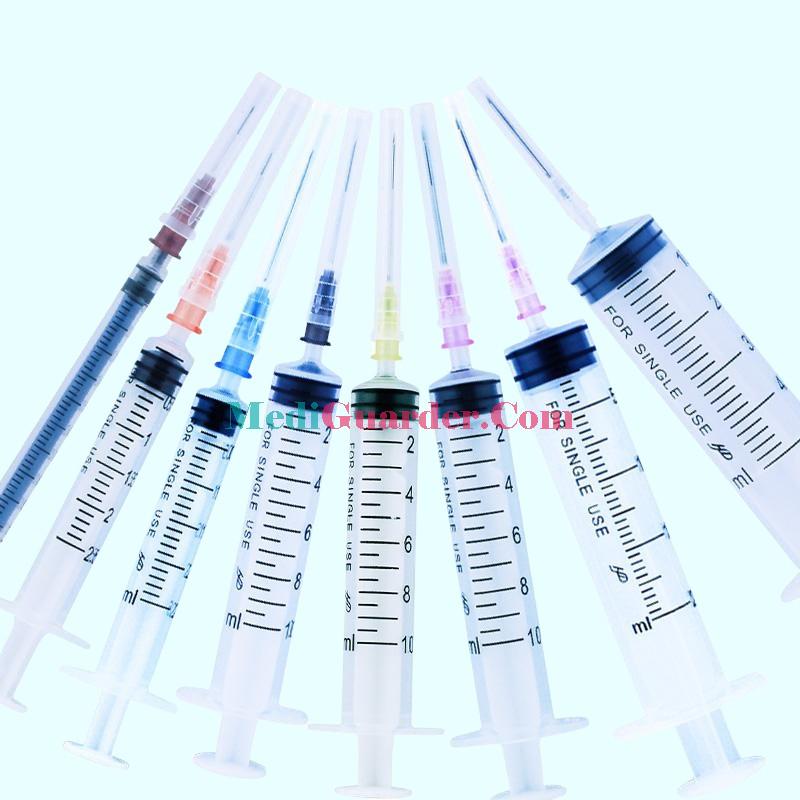
Different Specifications of Disposable Syringes
Disposable syringes come in a wide variety of specifications, mainly reflected in the differences in capacity and needle parameters.
Capacity Specifications: Common capacities include 1mL, 2mL, 5mL, 10mL, 20mL, 50mL, etc. 1mL and 2mL syringes are often used in scenarios with extremely high requirements for dosage accuracy, such as childhood vaccination and insulin injection. 5mL syringes are suitable for general drug injection and are frequently used in outpatient clinics and wards. Large – capacity syringes of 10mL and above are mostly used when a large – dose liquid infusion or special treatment (such as extracting joint effusion) is required.
Needle Specifications: Needle specifications are determined by thickness (outer diameter) and length. Commonly used thicknesses range from 26G (the thinnest) to 18G (thicker), and lengths range from 13mm to 51mm. Thin needles (such as 26G and 25G) are suitable for subcutaneous injection. For example, insulin injection can reduce the patient’s pain. Thicker needles (such as 21G and 20G) are used for intramuscular injection or when rapid drug injection is required, because the large – diameter can reduce the resistance of liquid medicine pushing. Long needles are used for deep – tissue injection. For example, for gluteal intramuscular injection, needles of 32mm or longer are often selected; short needles are used for shallow parts. For example, for intradermal injection, 13mm needles are generally used.
Usage Methods of Disposable Syringes and Needles
- Preparation Stage: Medical staff first check the name, dosage, expiration date, and other information of the drug to ensure its accuracy. Then, check whether the syringe packaging is intact, without damage or contamination. If the packaging is abnormal, it cannot be used.
- Drawing Liquid Medicine: Open the syringe packaging, hold the barrel, insert the needle into the rubber stopper of the medicine bottle, keep the needle bevel below the liquid level, and slowly pull the plunger to draw the required liquid medicine. During this period, pay attention to exhausting the air to ensure accurate dosage.
- Injection Operation: Select the appropriate site according to the injection method (intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular, or intravenous injection). After disinfection, pierce the skin at the correct angle. Intradermal injection is at a 5° angle to inject the liquid medicine between the epidermis and the dermis; subcutaneous injection is at a 30° – 40° angle to inject into the subcutaneous tissue; intramuscular injection is at a 90° angle to penetrate deep into the muscle layer; for intravenous injection, a suitable vein needs to be found and pierced at a 15° – 30° angle. Inject the liquid medicine slowly and closely observe the patient’s reaction.
Precautions
- Strict Aseptic Operation: The entire use process must follow the aseptic principle to avoid microbial contamination of the liquid medicine and syringe and reduce the risk of infection.
- Precise Dosage Control: Read the scales carefully to ensure that the dosage of the drawn and injected liquid medicine is accurate. Dosage deviation may affect the treatment effect and even endanger the patient’s life.
- Avoid Reuse: It is strictly prohibited to reuse a disposable syringe after use. Even if it has been used only once, factors such as residual liquid medicine and bacterial contamination may cause serious harm to subsequent users.
- Pay Attention to Needle Protection: Do not remove the needle cap too early before use to prevent the needle from being contaminated or stabbing others; immediately dispose of the needle after use to avoid accidental injury.
Correct Disposal of Disposable Syringe and Needle Waste
Used disposable syringes and needles belong to medical waste. If not properly disposed of, they will become a source of disease transmission and pollute the environment.
Classification and Collection: In medical institutions, used disposable syringes and needles should be immediately placed in special yellow medical waste sharps containers. The sharps containers need to be leak – proof, puncture – proof, and have obvious markings. It is strictly prohibited to mix syringes and needles with other domestic waste.
Centralized Transportation and Treatment: Medical institutions regularly transport the full sharps containers to the designated treatment site by professional medical waste transportation companies. The treatment method is mostly high – temperature incineration. High temperature can completely kill pathogens and harmlessly treat syringes and needles to avoid the spread of pollution.
Enhancing Public Awareness: For disposable syringe and needle waste generated by the public after self – injection (such as diabetics injecting insulin at home), it should also be properly disposed of. It can be placed in hard plastic bottles or other containers that are not easily pierced, marked as “medical waste”, and then handed over to local medical institutions or contact relevant departments for treatment. Do not discard it casually.
Although medical disposable syringes seem simple, they play an irreplaceable role in the medical field. Correctly understanding their specifications, mastering usage methods and precautions, and properly disposing of used waste are key measures to ensure medical safety and maintain public health, which is of great significance for promoting the healthy development of the medical cause.
 China Disposable Medical Supplies, Medical Consumables Supplier
China Disposable Medical Supplies, Medical Consumables Supplier